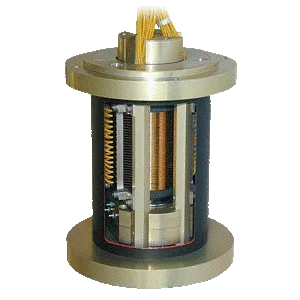
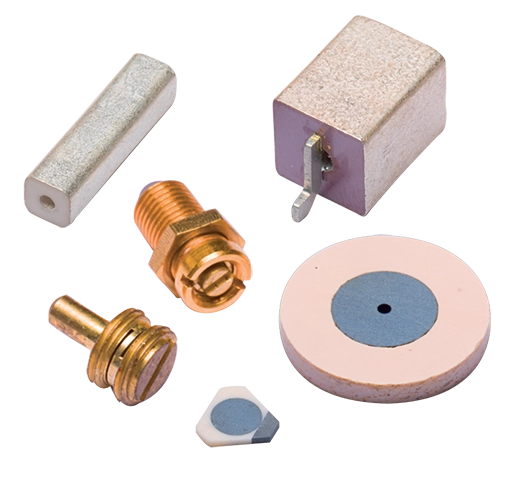
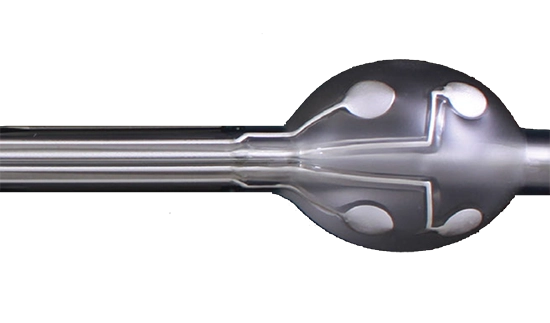
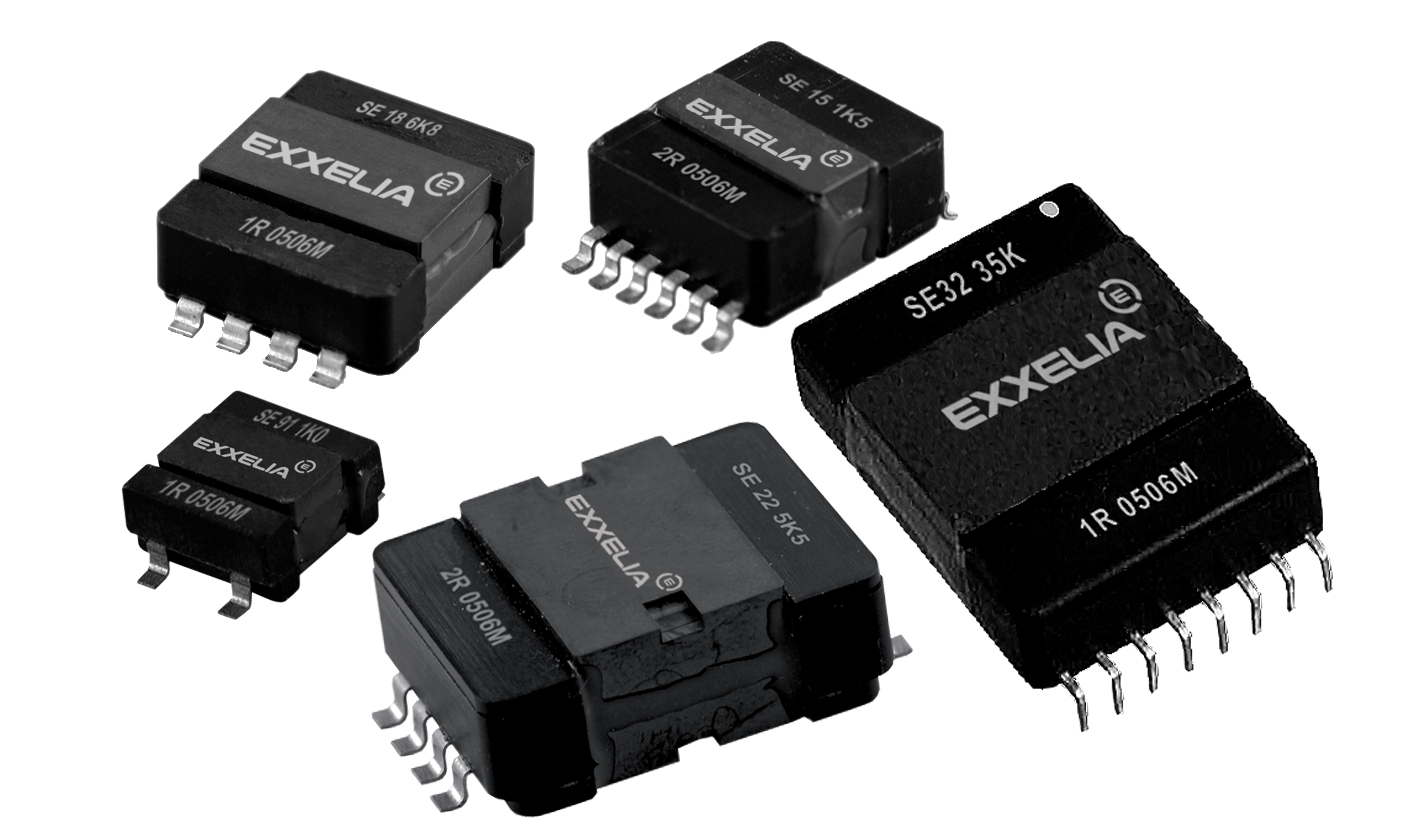
Power Inductors
Filtre
Operating Temp
-55°C
125°C
Mounting
SMD
Frequency
1MHz
Winding flat wire on flange / Helical winding
Custom example
C Cores Assemblies (Inductors)
High temperature
Operating Temp
240°C
Height
300mm
Frequency
50Hz
500Hz
|
Name
|
Download
|
Operating Temp
|
Height
|
Mounting
|
Frequency
|
Power
|
Current
|
Inductance
|
Peak Current
|
RoHS
|
Accuracy
|
Ratio
|
Diameter (Outside Diameter)
|
Length
|
Weight
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCM Series (Chameleon Concept Magnetics) | -55°C ~ 125°C | - | SMD | 1MHz | - | 17.7A | 1µH ~ 4679µH | 22.1A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SESI Series | -55°C ~ 125°C | - | SMD | 1MHz | - | 0.045A ~ 24A | 1µH ~ 6800µH | 27.6A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Power supply inductor | -40°C ~ 180°C | - | - | 50Hz | - | 60A | 600µH | 70A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Custom inductor | -40°C ~ 180°C | - | - | 50Hz | - | 242A | 150µH | 280A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Filtering Choke | -40°C ~ 180°C | - | - | 60Hz | - | 150A | 1.1mH | 175A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Harmonic Choke 50Hz | -40°C ~ 180°C | - | - | 60Hz | - | 117A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Battery inductor 50Hz | -40°C ~ 180°C | - | - | 50Hz | - | 600A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ESI 01 | -55°C ~ 125°C | - | - | 1MHz | - | 0.26A ~ 2.1A | 2.69µH ~ 151.2µH | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ESI 07 | -55°C ~ 125°C | - | - | 1MHz | - | 0.6A ~ 2.9A | 0.42µH ~ 8.42µH | 6A | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Winding flat wire on flange / Helical winding | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Shaped Ferrite assembly | 0°C ~ 240°C | - | - | 1MHz | - | 60A ~ 270A | 5µH ~ 20000µH | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Overmolded Cores Assembly (Inductors) | - | 320mm | - | 12kHz | - | 0A ~ 316A | 30µH | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| C Cores Assemblies (Inductors) | 240°C | 300mm | - | 50Hz ~ 500Hz | - | 2A ~ 240A | 600µH ~ 3mH | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
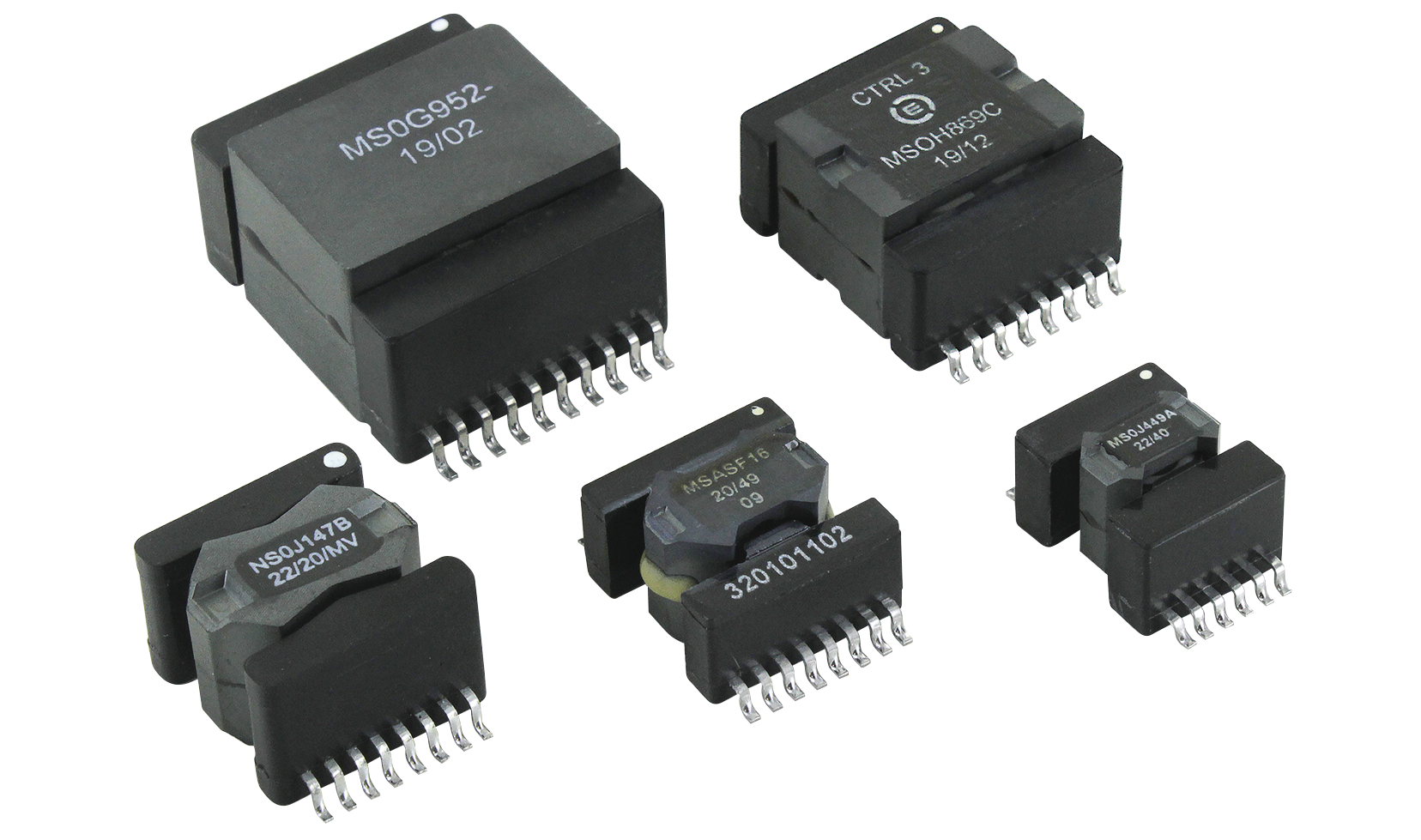
CCM Series (Chameleon Concept Magnetics)

SESI Series

Power supply inductor
Custom example
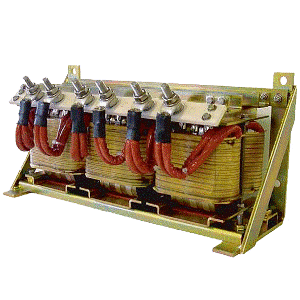
Custom inductor
Custom example

Filtering Choke
Custom example

Harmonic Choke 50Hz
Custom example

Battery inductor 50Hz
Custom example
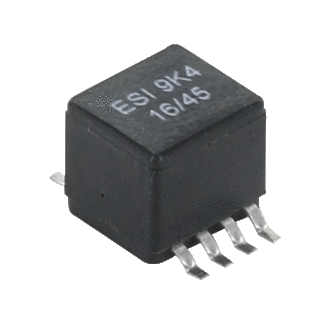
ESI 01

ESI 07

Winding flat wire on flange / Helical winding
Custom example

Shaped Ferrite assembly
Custom example

Overmolded Cores Assembly (Inductors)
Custom example

C Cores Assemblies (Inductors)
High temperature
Power Inductors
Our high-quality power inductors components ensure optimal performance and reliability in your applications. From compact designs for space-constrained environments to high-current handling capabilities for robust power systems, our power inductors cater to diverse needs.
Whether you're designing power converters, DC-DC converters, or voltage regulators, Exxelia's power inductors deliver exceptional performance to drive innovation forward.

Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to the most frequently asked questions about our products and services.
Still have questions ?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for ? Please contact with our customer service
Contact