Exxelia will integrate a cobot into its manufacturing process
In recent days, artificial intelligence has been at the center of the news, and will soon be deployed in Exxelia's production workshops, with the integration of technology related to cobots.

Exxelia has just equipped itself with a cobot (in partnership with the company Cognitive Engines) adapted to the production needs related to the manufacture of RF High Q capacitors.
The cobot is a collaborative robot designed to work hand-in-hand with operators. This technology coupled with artificial intelligence (I.A) offers a multitude of advantages including:
- Quality improvement: The cobots are equipped with high performance sensors and integrated quality control systems, which allow 100% thorough visual inspection, and guarantee a high level of quality, while adapting to the movements of the operators (no occupational safety risk).
- Flexibility: Cobots are lightweight and adaptable. This versatility allows them to occupy different positions depending on the needs of the moment.
- Safety: Cobots are designed to be used in pairs with Exxelia operators and can therefore protect them from dangerous or arduous tasks, which greatly improves the quality of life at work (reduction of repetitive gestures; positive impact on musculoskeletal disorders ).
- Optimization of operator time: Cobots take care of low value-added tasks and let the operator focus on high-value tasks, which values the contribution of operators.
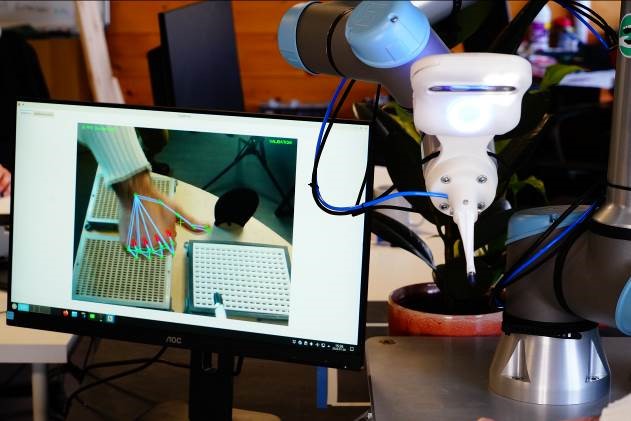

By collaborating with operators, cobots can improve production quality and accuracy, while ensuring their safety.
Industry 4.0 is changing the way businesses operate and the way products are designed, manufactured and delivered. Exxelia is convinced of the importance of Industry 4.0 and is positioning itself to be at the forefront of this transformation.
As a company specializing in the design and manufacture of critical electronic components for industrial applications, Exxelia pays particular attention to maintaining its extensive know-how. Exxelia uses state-of-the-art technologies to ensure the high level of quality that the applications the group serves cannot be without. The group pays particular attention to the coexistence of robotization with the mastery of manual processes held by operators to continue to offer customers the highest quality products, while remaining competitive.
Adopting this technology will allow Exxelia to maintain its leadership position in its industry, while improving quality, accuracy, operator safety and production efficiency.